The Lebanese Druze leader – who fought in a 15-year civil war that redrew the map of Lebanon – believes that the new battles for Sunni Muslim jihadi control of northern and eastern Syria and western Iraq have finally destroyed the post-World War Anglo-French conspiracy, hatched by Mark Sykes and François Picot, which divided up the old Ottoman Middle East into Arab statelets controlled by the West.
The Islamic Caliphate of Iraq and Syria has been fought into existence – however temporarily – by al-Qa’ida-affiliated Sunni fighters who pay no attention to the artificial borders of Syria, Iraq, Lebanon or Jordan, or even mandate Palestine, created by the British and French. Their capture of the city of Mosul only emphasises the collapse of the secret partition plan which the Allies drew up in the First World War – for Mosul was sought after for its oil wealth by both Britain and France. Keep reading >>>>>
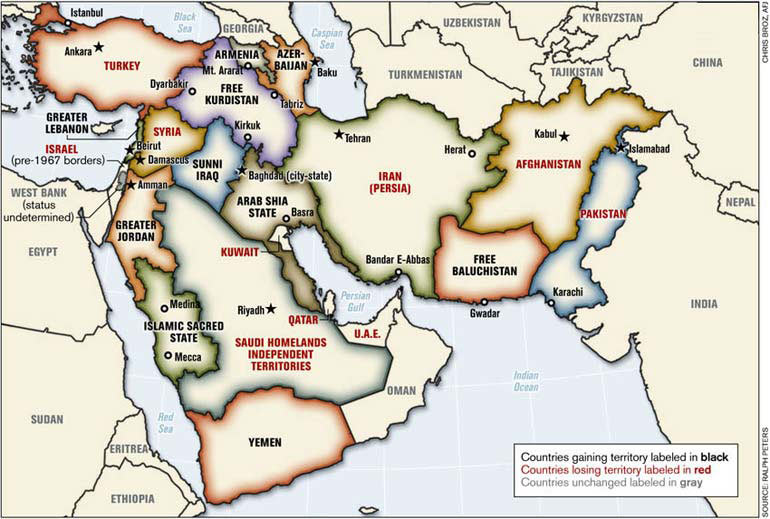
NATO Re-surfaced Map of the New Middle East
By: Chris_Kitze
Mahdi Darius Nazemroaya writes: A relatively unknown map of the Middle East, NATO-garrisoned Afghanistan, and Pakistan has been circulating around strategic, governmental, NATO, policy and military circles since mid-2006. It has been causally allowed to surface in public, maybe in an attempt to build consensus and to slowly prepare the general public for possible, maybe even cataclysmic, changes in the Middle East. This is a map of a redrawn and restructured Middle East identified as the “New Middle East.”
“Hegemony is as old as Mankind…” -Zbigniew Brzezinski, former U.S. National Security Advisor
The term “New Middle East” was introduced to the world in June 2006 in Tel Aviv by Former U.S. Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice (who was credited by the Western media for coining the term) in replacement of the older and more imposing term, the “Greater Middle East.”
This shift in foreign policy phraseology coincided with the inauguration of the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan (BTC) Oil Terminal in the Eastern Mediterranean. The term and conceptualization of the “New Middle East,” was subsequently heralded by the U.S. Secretary of State and the Israeli Prime Minister at the height of the Anglo-American sponsored Israeli siege of Lebanon. Prime Minister Olmert and Secretary Rice had informed the international media that a project for a “New Middle East” was being launched from Lebanon.
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Humanity, Religion, Culture, Ethics, Science, Spirituality & Peace
http://PeaceForumNet.blogspot.com
http://AftabKhan.blog.com
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *...
http://AftabKhan.blog.com
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *...
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *


